As technology advances rapidly, the need for secure communication becomes more crucial than ever. The risk of cyberattacks and data breaches is a major concern for businesses and individuals alike. This is where quantum cryptography comes into play, providing a new level of security that is almost impossible to hack.
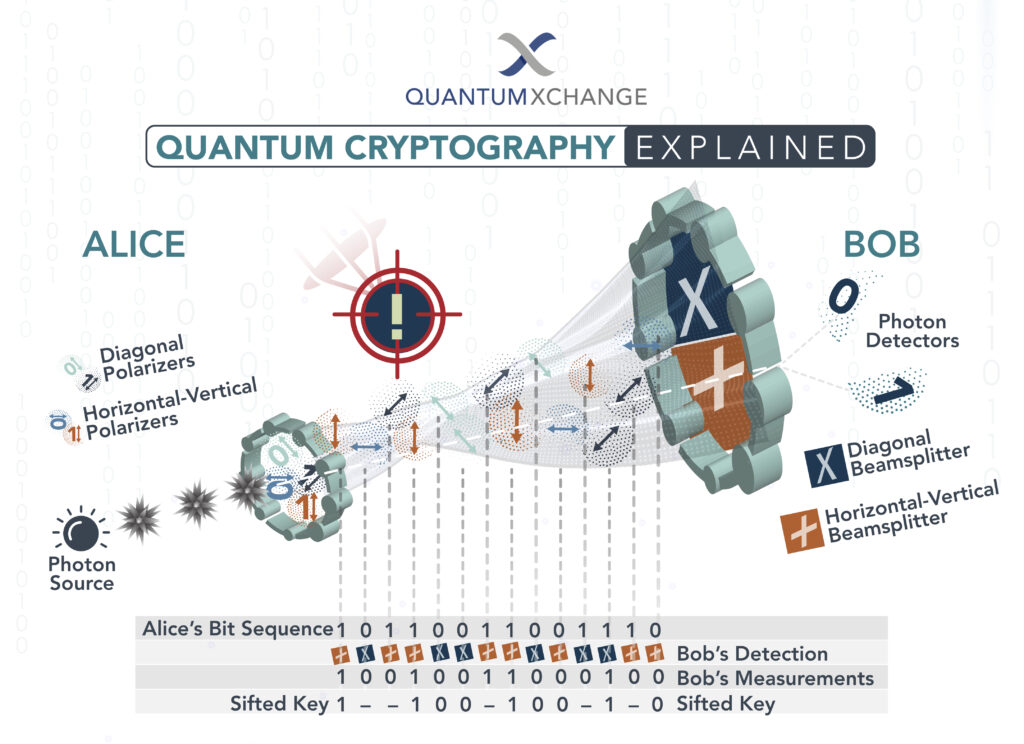
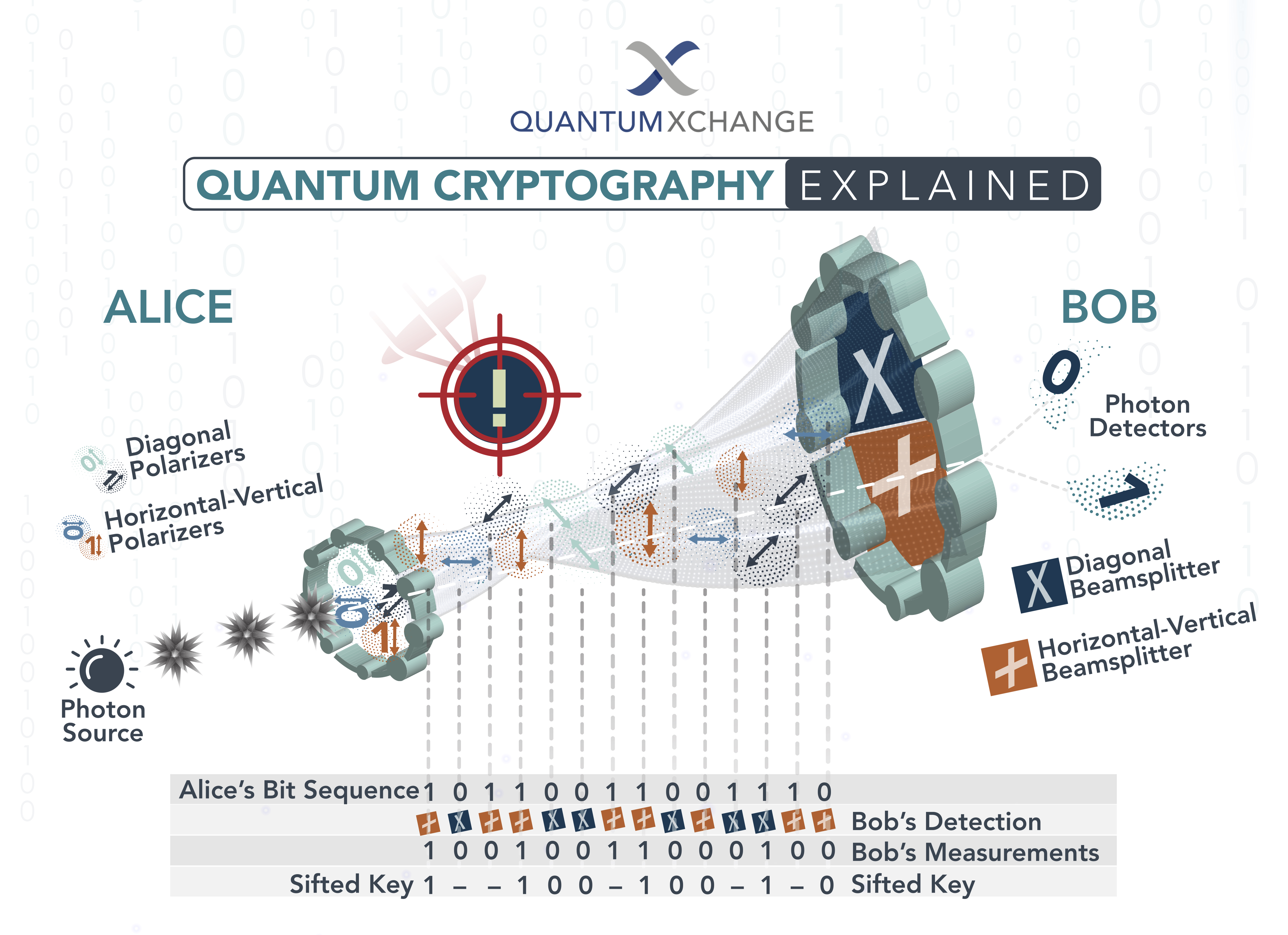
Unlike traditional cryptography methods that rely on mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography uses the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data. The process involves the use of quantum key distribution (QKD) to transmit a secret key between two parties. This key is then used to encrypt and decrypt messages, ensuring that only the intended recipient can access the data. But how exactly does quantum cryptography work, and what makes it so secure? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating topic in more detail.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a form of cryptography that uses quantum mechanical principles to secure communications. It is based on the principles of quantum mechanics, which makes it virtually impossible for unauthorized parties to access data. Quantum cryptography can be used to secure data and provide authentication of both parties involved in a communication. It is also used to securely exchange keys for encryption and decryption.
Quantum cryptography utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to transmit information securely. It works by encoding data in the form of photons, which are then sent between two points. The photons are then measured at each point, allowing the data to be securely transmitted. Quantum cryptography is considered to be one of the most secure forms of encryption available.
How is Quantum Cryptography Used to Secure Data?
Secure Key Exchange
Quantum cryptography can be used to securely exchange encryption keys between two parties. This is done by encoding the encryption keys in the form of photons, which are then sent between the two points. The photons are then measured at each point, allowing the parties to securely exchange the encryption keys.
The key exchange process is secure because the photons are encoded in such a way that any attempts to intercept or tamper with the data will be detected. This makes it virtually impossible for an unauthorized party to access the data. This ensures that the information is secure and can only be accessed by the intended parties.
Secure Data Transmission
Quantum cryptography can also be used to securely transmit data. This is done by encoding the data in the form of photons, which are then sent between two points. The photons are then measured at each point, allowing the data to be securely transmitted. The data is then encrypted using the encryption keys that were securely exchanged in the key exchange process.
The data transmission process is secure because the photons are encoded in such a way that any attempts to intercept or tamper with the data will be detected. This makes it virtually impossible for an unauthorized party to access the data. This ensures that the data is secure and can only be accessed by the intended parties.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is a security technique that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data. It is used to protect information from being intercepted by malicious third parties.
What is quantum cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a security technique that utilizes the principles of quantum mechanics to secure data from being intercepted by malicious third parties. This is done by encoding the data using quantum-mechanical properties, such as the polarization or spin of photons. The data is then transmitted using a secure quantum channel, which is encrypted using a quantum key. The encrypted data is then decoded by the intended recipient.
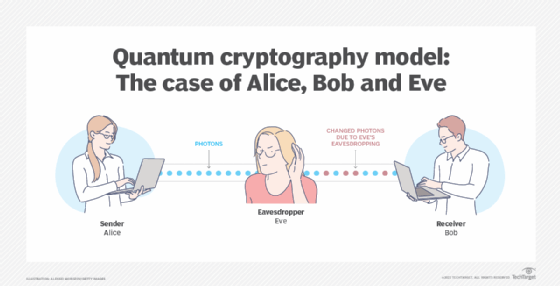
Quantum cryptography is a particularly secure form of encryption because it is impossible to intercept or break the encryption without being detected. This is because any attempt to access the data will change the quantum state of the photons, which can be detected by the sender and receiver.
How is quantum cryptography used?
Quantum cryptography is used to secure data transmissions between two parties, such as in banking and financial transactions, government communications, and military applications. It is also used to protect sensitive data stored on computers, such as medical records and financial information.
Quantum cryptography is also used to secure data transmitted over public networks, such as the Internet. This is done by encrypting the data using a quantum key, which is then transmitted over a secure channel. The data can then only be decrypted by the intended recipient, who has the key. This ensures that the data is secure and cannot be intercepted by malicious third parties.
What are the advantages of quantum cryptography?
The main advantage of quantum cryptography is that it is virtually impossible to break or intercept the encryption without being detected. This makes it one of the most secure forms of encryption currently available. Additionally, quantum cryptography is fast and efficient, and can be used to securely transmit large amounts of data in a short period of time.
Another advantage of quantum cryptography is that it is easy to use and implement. It does not require complex hardware or software, and can be integrated into existing networks and systems.
What are the disadvantages of quantum cryptography?
The main disadvantage of quantum cryptography is that it is very expensive to implement. It requires specialized hardware and software, as well as highly skilled personnel to operate it. Additionally, quantum cryptography is only effective over short distances, which limits its use in certain applications.
Another disadvantage of quantum cryptography is that it is vulnerable to quantum hacking. This is where an attacker can use quantum computing to break the encryption and access the data.
What is the future of quantum cryptography?
The future of quantum cryptography is very promising. As technology advances, quantum cryptography will become more reliable, secure, and cost-effective. It will also be used in a wider range of applications, such as securing data transmitted over longer distances and protecting data stored on computers.
In the future, quantum cryptography will also be used to protect data in the cloud, as well as data sent through satellites. This will allow organizations to securely store and transmit large amounts of data quickly and securely.
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a groundbreaking technology that provides an innovative approach to securing data. With the rise of cyber threats and data breaches, this technology offers a solution to prevent unauthorized access and interception of sensitive information. Quantum cryptography is based on the principles of quantum mechanics and uses the properties of quantum particles to create unbreakable codes, making it an ideal solution for organizations and individuals who require high levels of security.
As quantum cryptography continues to evolve, it has the potential to revolutionize the way we secure our data. Its ability to provide secure communication channels and prevent eavesdropping is a game-changer for industries such as finance, healthcare, and government agencies. While the technology is still in its early stages, the potential benefits are significant, and we can expect to see more widespread adoption of quantum cryptography in the coming years. As we move towards a more connected world, quantum cryptography offers a promising solution to protect our sensitive information and keep it safe from prying eyes.