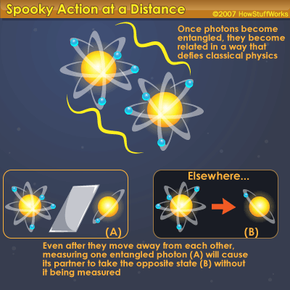
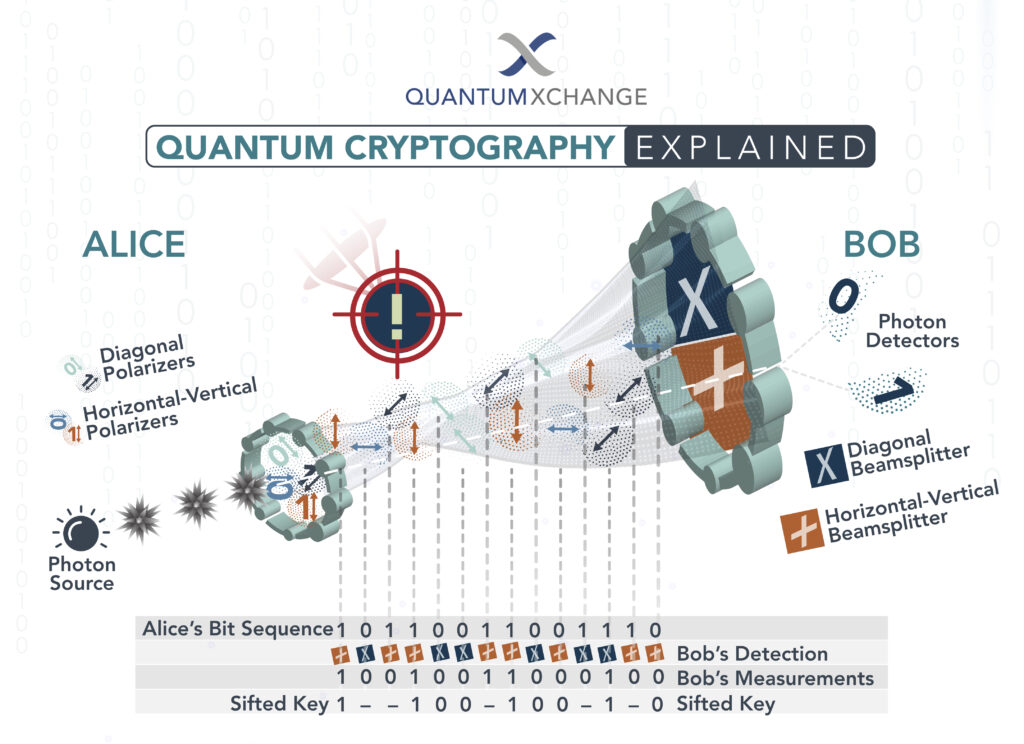
Quantum cryptography is a fascinating field that has been gaining popularity in the past few years. Unlike traditional cryptography, which is based on mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography is based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is a method of encrypting information that is theoretically impossible to break, making it one of the most secure forms of communication.
At its core, quantum cryptography relies on the properties of quantum particles, such as photons, to create a secure key for encrypting and decrypting messages. The process involves sending a stream of photons between two parties, with each photon representing a single bit of information. The randomness of these photons, as well as the fact that they cannot be copied without being detected, makes it impossible for an eavesdropper to intercept the message without being detected. In this article, we will explore how quantum cryptography works, its applications, and its potential impact on the future of communication and security.
Quantum cryptography is a secure communication method that uses quantum mechanics to encrypt and protect data. It uses the principles of quantum entanglement and superposition to create a secure, shared key between two users. This key is then used to encrypt and decrypt messages sent between the two users. Quantum cryptography is more secure than traditional cryptography because it is impossible to eavesdrop on the communication without being detected.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a form of secure communication based on the principles of quantum mechanics. It is a revolutionary new way to protect data and communications from interception and tampering. It utilizes the laws of physics to provide an unbreakable level of security that is virtually impossible to bypass.
Quantum cryptography is a powerful tool in the fight against cyber-crime, espionage, and other forms of malicious activity. It provides a secure communication channel that is virtually unhackable, allowing users to communicate and transact with complete confidence.
How does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using quantum states to encode data and transmit it securely over a communication channel. This technique relies on the principles of quantum mechanics, which state that a quantum state cannot be observed without changing it. As such, any attempts to eavesdrop on the communication will be immediately detected, and the data will remain secure.
The process of quantum cryptography begins with the sender of the data generating a random string of binary numbers or “bits” and encoding them in a quantum state. The quantum state is then sent to the receiver over a secure channel. The receiver then uses a quantum measurement device to measure the quantum state and decode the data. If the data has been intercepted, the measurement process will detect the intrusion and the data will remain secure.
Benefits of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography offers several advantages over traditional methods of encryption. For one, it is virtually unhackable. Any attempts to intercept the data will be detected and the data will remain secure. Additionally, quantum cryptography is much faster than traditional methods, allowing users to securely transmit large amounts of data quickly and efficiently.
Another key benefit of quantum cryptography is the ability to detect and prevent tampering. This is important for ensuring the integrity of data and communications. Quantum cryptography can also be used to detect and prevent malicious activities such as espionage and cyber-crime.
Finally, quantum cryptography is highly scalable and can be used for both small and large-scale applications. This makes it ideal for use in a variety of contexts and for a variety of users.
Limitations of Quantum Cryptography
Despite its numerous advantages, quantum cryptography does have some limitations. For one, it requires specialized equipment to generate and measure the quantum states, which can be expensive and difficult to obtain. Additionally, the process of generating and measuring the quantum states can be time-consuming and complex.
Furthermore, quantum cryptography is still relatively new and is still being developed. As such, there may be some issues that have not yet been addressed. Finally, quantum cryptography is not suitable for all applications and may not be suitable for certain types of data or communications.
Applications of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography has many potential applications in the world of secure communication. It can be used to secure financial transactions, protect private data, and provide secure communication channels for businesses, governments, and other organizations. Additionally, quantum cryptography can be used to detect and prevent malicious activities such as espionage and cyber-crime.
In addition, quantum cryptography can be used for quantum computing applications. This includes quantum key distribution, quantum secure communication, and quantum authentication. Quantum cryptography can also be used to secure data stored in quantum computers.
Future of Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a revolutionary new technology that has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that quantum cryptography will become more widely used and more accessible. It is also likely that quantum cryptography will become more affordable and more secure.
In the future, quantum cryptography could be used to securely transmit data over long distances, create secure communication networks, and protect data stored in quantum computers. Additionally, quantum cryptography could be used to detect and prevent malicious activities such as espionage and cyber-crime.
Ultimately, quantum cryptography has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate and protect data. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that quantum cryptography will become more widely used and more accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Quantum cryptography is a type of encryption that uses quantum mechanics to secure communications between two parties. It is considered to be the most secure form of cryptography available today.
What is Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a method of encrypting messages using quantum mechanics. It is a form of quantum cryptography that uses quantum mechanical properties such as entanglement and superposition to secure communications between two parties. It is considered to be the most secure form of cryptography, as it is impossible for a third-party to intercept or decode the message without being detected.
Quantum cryptography relies on the principles of quantum mechanics to generate a secure key for the transmission of data. The key is generated using the properties of quantum particles, such as photons, which can exist in multiple states at the same time. This ensures that the key cannot be intercepted or decoded by a third party, as any attempt to do so would be detected and the encryption algorithm would be changed.
How does Quantum Cryptography Work?
Quantum cryptography works by using the principles of quantum mechanics to generate and transmit a secure key between two parties. This key is generated using the properties of quantum particles, such as photons, which can exist in multiple states at the same time. The key is transmitted over a secure channel and is used to encrypt the data.
Once the key is generated, the two parties can exchange messages securely, as any attempt to intercept or decode the message would be detected and the encryption algorithm would be changed. This ensures that the data is secure and cannot be accessed by a third party.
What are the Benefits of Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography has a number of benefits over traditional forms of encryption. It is the most secure form of encryption available today, as it is impossible for a third-party to intercept or decode the message without being detected. It also offers the ability to securely transmit data over long distances, as the key is generated using the properties of quantum particles which can exist in multiple states at the same time.
Another benefit of quantum cryptography is that it is resistant to quantum computing attacks. Traditional encryption algorithms are vulnerable to quantum computing attacks, which can break the encryption and allow the data to be accessed. Quantum cryptography is resistant to these attacks, as any attempt to break the encryption algorithm would be detected and the encryption algorithm would be changed.
What are the Limitations of Quantum Cryptography?
The main limitation of quantum cryptography is that it requires specialized hardware and is expensive to implement. Additionally, quantum cryptography is limited to point-to-point communications, meaning that it cannot be used for large-scale networks.
Another limitation is that quantum cryptography is not yet widely used, as it is still in the early stages of development. Additionally, there are some theoretical attacks on quantum cryptography that have not yet been tested in practice.
What is the Future of Quantum Cryptography?
The future of quantum cryptography is bright, as it is considered to be the most secure form of encryption available today. It is expected to continue to evolve and become more widely used in the future, as it is resistant to quantum computing attacks and offers the ability to securely transmit data over long distances.
Additionally, quantum cryptography is expected to become easier to implement, as the technology continues to develop and become more accessible. The cost of implementation is also expected to decrease as more companies embrace quantum cryptography and the hardware required becomes more widely available.
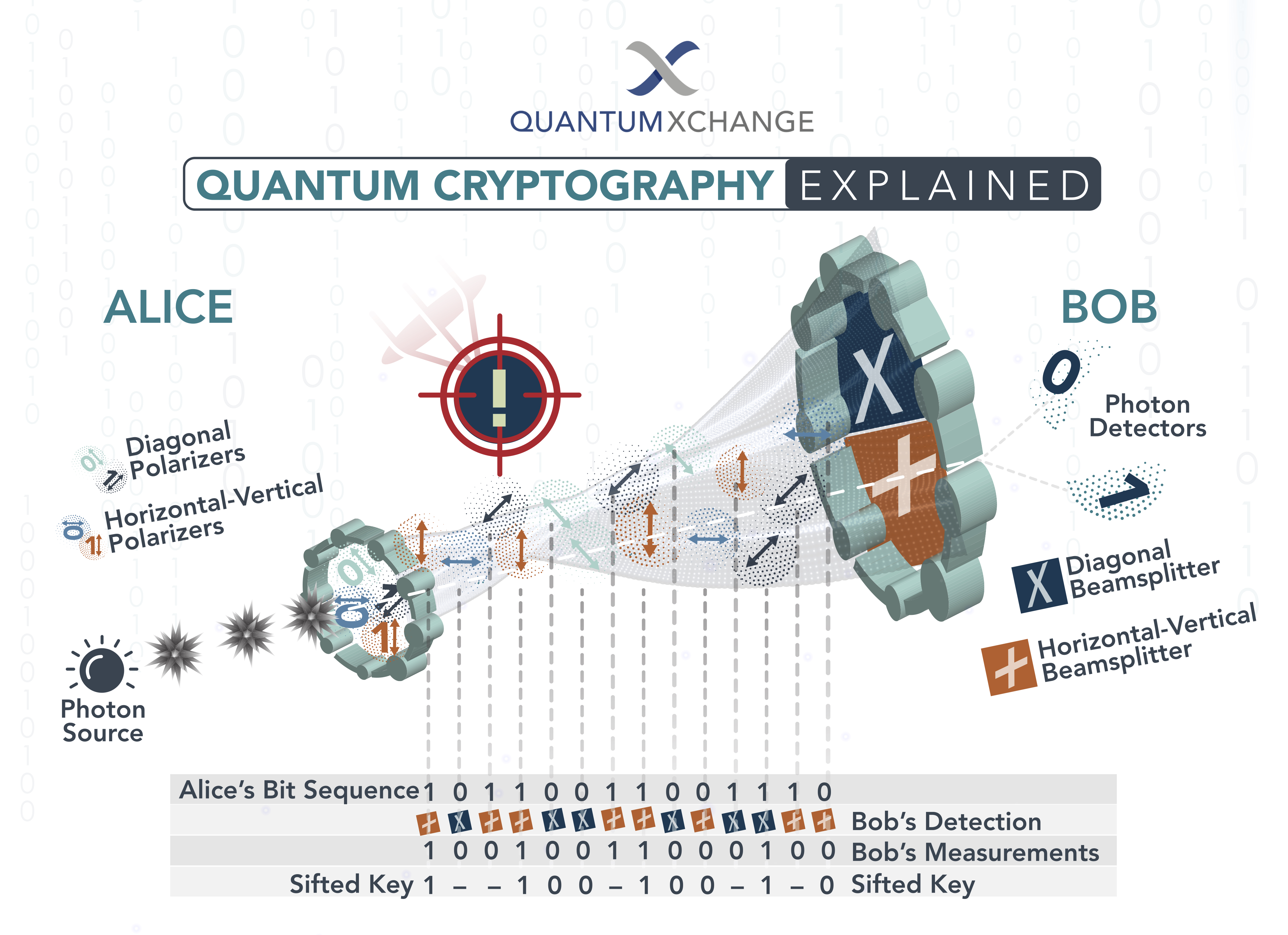
In conclusion, quantum cryptography is a fascinating and rapidly evolving field that holds great promise for secure communication in the digital age. With its foundation in the principles of quantum mechanics, this technology offers a new and highly secure method of encryption that is nearly impossible to hack or intercept. As quantum cryptography continues to advance, we can expect to see it implemented in a wide range of applications, from top-secret government communications to online banking and e-commerce.
As we move into an increasingly connected world, the need for secure communication has never been more pressing. Quantum cryptography offers a solution that is both highly secure and adaptable to a wide range of applications. While there are still challenges to overcome in terms of cost and scalability, the potential benefits of this technology are enormous. With further research and development, quantum cryptography may soon become a standard feature of our digital lives, enabling us to communicate with confidence and security in a world that is constantly evolving.