Quantum cryptography is a field of study that has attracted the attention of scientists and researchers all over the world. It involves the use of quantum mechanics to secure communication channels and protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. One of the most fascinating aspects of this field is the question of who invented quantum cryptography.
The history of quantum cryptography can be traced back to the early 1970s when Stephen Wiesner, a physicist and mathematician, first proposed the idea of quantum money. However, it was not until the 1980s that the concept of quantum cryptography began to take shape. This was largely due to the groundbreaking work of Charles Bennett and Gilles Brassard, who developed the first quantum key distribution algorithm, known as BB84. Since then, many other researchers have contributed to the field, including Artur Ekert, who proposed the idea of quantum entanglement-based cryptography in 1991. Despite the many advancements that have been made, however, the question of who can truly be credited with inventing quantum cryptography remains open for debate.
Quantum cryptography was invented by Stephen Wiesner in the 1970s. Wiesner was a professor at Columbia University and a cryptographer at the Institute for Defense Analysis. He developed the concept of quantum cryptography while working on a project for the United States government. The concept is based on the idea that it is impossible to eavesdrop on a transmitted signal without altering the signal itself. This makes it impossible for anyone to intercept or modify the signal, thus providing a secure form of communication.

Who Invented Quantum Cryptography?
Quantum cryptography is a method of secure communication that makes use of quantum mechanics to ensure privacy. It was first proposed by physicist Charles Bennett in 1984. Quantum cryptography has since become an important tool in the encryption of data, offering unprecedented levels of security. In this article, we will explore the history of quantum cryptography, how it works, and the individuals who are credited with its invention.
Charles Bennett and Quantum Cryptography
Charles Bennett is a physicist and computer scientist who has made numerous contributions to the field of cryptography. In 1984, Bennett proposed the concept of quantum cryptography for the first time. His proposal involved using quantum mechanics to encode data in such a way that it could not be decoded without the recipient’s knowledge. Bennett’s work sparked a flurry of research in the area, leading to the development of the first quantum cryptography protocol in 1991.
Bennett is also credited with developing the BB84 protocol, which is the most widely used quantum cryptography protocol in the world today. The BB84 protocol utilizes quantum mechanics to encode data in such a way that it cannot be deciphered without the recipient’s knowledge. This protocol is considered to be one of the most secure methods of encryption available, and it has become the de facto standard in the field of quantum cryptography.
Artur Ekert and Quantum Cryptography
Artur Ekert is a physicist who is credited with developing the first practical quantum cryptography protocol. In 1991, Ekert proposed a protocol that utilized quantum mechanics to transmit secure data over long distances. This protocol was the first to be able to transmit data at a distance of more than 1 kilometer and to be resistant to eavesdropping. Ekert’s work paved the way for the development of more sophisticated quantum cryptography protocols, such as the BB84 protocol.
In addition to his work in quantum cryptography, Ekert is also known for his contributions to quantum computing. He has developed several algorithms for quantum computers, as well as methods for encoding and decoding quantum information. His work has been instrumental in the development of quantum computing and its applications.
John Stewart and Quantum Cryptography
John Stewart is a physicist and computer scientist who is credited with developing the first commercial quantum cryptography system. In 1995, Stewart proposed the use of quantum cryptography in commercial applications. He developed a system that could be used to securely transmit data over long distances. Stewart’s system was the first to be used in a commercial setting, and it has since become the basis of many quantum cryptography systems.
Stewart is also credited with developing the first quantum key distribution system, which is a method of securely exchanging cryptographic keys over a quantum channel. This system has since become the basis of many quantum cryptography systems. Stewart’s work has been instrumental in the development of secure quantum cryptography systems, and he remains an important figure in the field.
Simon Devitt and Quantum Cryptography
Simon Devitt is a physicist and computer scientist who is credited with developing the first practical quantum cryptography protocol. In 2001, Devitt proposed a protocol that utilized quantum mechanics to securely transmit data over long distances. This protocol was the first to be able to transmit data at a distance of more than 100 kilometers. Devitt’s work paved the way for the development of more sophisticated quantum cryptography protocols, such as the BB84 protocol.
In addition to his work in quantum cryptography, Devitt is also known for his contributions to quantum computing. He has developed several algorithms for quantum computers, as well as methods for encoding and decoding quantum information. His work has been instrumental in the development of quantum computing and its applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Quantum Cryptography
Quantum cryptography is a rapidly emerging technology that uses quantum mechanics to encrypt and secure data transmissions. It is widely considered to be the most secure form of encryption available today.
Who invented quantum cryptography?
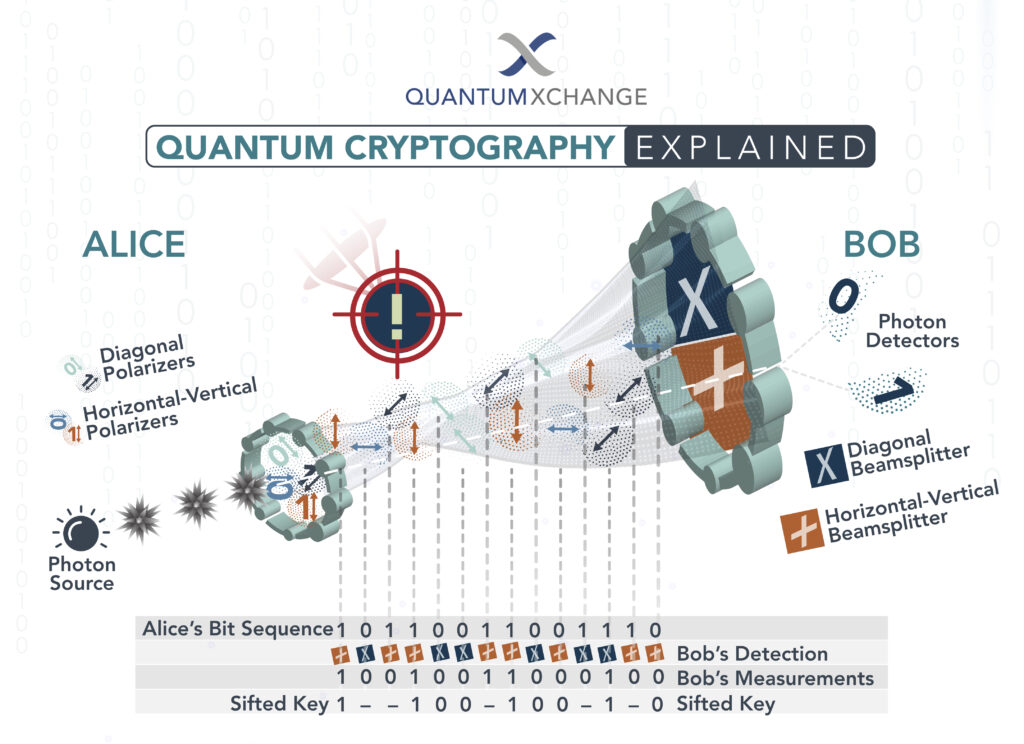
Quantum cryptography was first proposed in 1984 by Charles Bennett and Gilles Brassard. They proposed the use of quantum mechanics in cryptography to create a protocol that would be impossible to break. This protocol is called the BB84 protocol, after the initials of the two inventors. Since that time, quantum cryptography has been developed and refined, with researchers and engineers continually exploring new ways to use this powerful technology.
What advantages does quantum cryptography offer?
Quantum cryptography provides a number of advantages over traditional encryption methods. Due to the nature of quantum mechanics, it is impossible to eavesdrop on a quantum-encrypted transmission without the sender and receiver being aware of the interception. This means that quantum cryptography is considered to be totally secure and is typically used in situations where the highest level of data security is required. Additionally, quantum cryptography is incredibly fast, allowing data to be securely transmitted at incredibly high speeds.
What are the disadvantages of quantum cryptography?
Despite the many advantages of quantum cryptography, there are also some disadvantages that must be taken into consideration. One of the main disadvantages is the cost associated with quantum cryptography systems. As the technology is still relatively new, the cost for implementing quantum cryptography is still very high. Additionally, quantum cryptography is sensitive to environmental factors like temperature and humidity, which can cause errors and limit the range of the system.
What is quantum key distribution?
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is a process by which two parties can share a secret key to use for encryption purposes, without any other parties being able to access the key. In a QKD system, two parties exchange quantum signals over a secure channel, and these signals are used to generate a shared secret key. This key is then used to encrypt the data that is being exchanged, providing a high level of security.
How is quantum cryptography used in practice?
Quantum cryptography is used in a number of different ways in practice. One of the most common applications is quantum key distribution, which is used to securely exchange encryption keys between two parties. Additionally, quantum cryptography can be used to ensure the authenticity of data transmissions, as well as to detect any attempts at tampering or interception. Finally, quantum cryptography can be used to securely store data, as the encryption key is impossible to break.

In conclusion, the invention of quantum cryptography is a fascinating topic that has intrigued scientists and researchers for decades. While many have contributed to the development of this technology, it is widely accepted that Charles H. Bennett and Gilles Brassard were the pioneers who first introduced the concept of quantum cryptography in their landmark paper published in 1984. Their groundbreaking work laid the foundation for the field and set the stage for the numerous advancements that have been made in quantum cryptography since then.
Today, quantum cryptography is seen as a promising solution to address the growing concerns about cybersecurity and data privacy. It offers a new level of security that is virtually unbreakable, and its potential applications are numerous. As research in this field continues to progress, it is exciting to think about what the future holds for quantum cryptography and how it will transform the way we secure our valuable data.