As technology continues to evolve, so do the methods of cryptography used to secure our data. One of the most popular methods of encryption, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), has been widely adopted due to its high level of security and efficiency. However, with the emergence of quantum computers, concerns have been raised regarding the effectiveness of ECC. The question on everyone’s mind is whether elliptic curve cryptography is quantum secure.
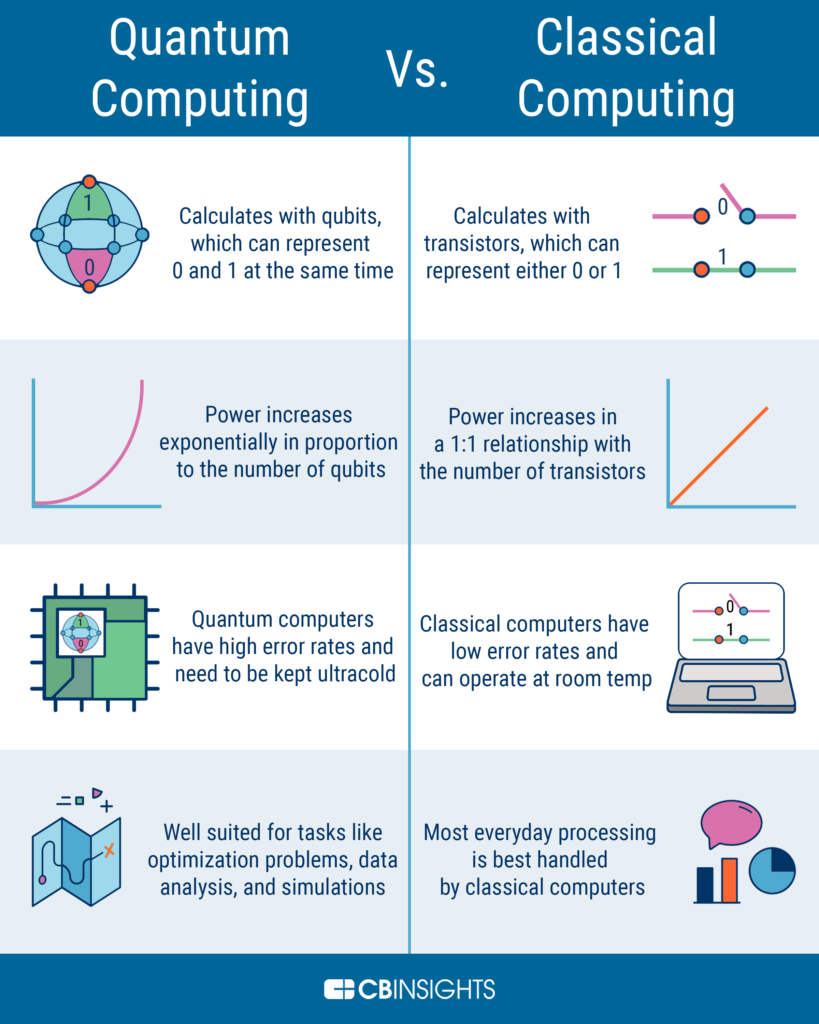
Quantum computers are incredibly powerful machines that can solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers. This means that they can break traditional encryption methods that are currently in use, leaving many people wondering whether ECC is secure against quantum attacks. This has led to numerous studies and researches to determine whether elliptic curve cryptography can stand up to the power of quantum computers. In this article, we will explore the security of ECC and its vulnerability against quantum attacks.
Introduction to Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
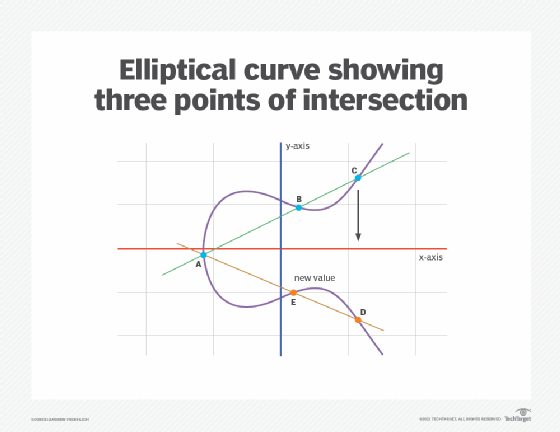
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a public-key cryptography technology that provides users with an added layer of security when using digital transactions. This technology uses a mathematical equation and elliptic curve to encrypt and decrypt data. It is considered to be one of the most secure forms of cryptography and is used by many organizations and governments as an effective form of encryption.
Is Elliptic Curve Cryptography Quantum Secure?
How ECC works
ECC uses a mathematical equation to generate a pair of public and private keys. The public key is used to encrypt data while the private key is used to decrypt the data. This process is based on the properties of elliptic curves which are used to generate the keys. The main idea behind this technology is that the public key is made available to everyone, but only the private key is known to the user. This ensures that only the user can decrypt the data.
Risks of ECC
One of the major risks of using ECC is the potential for quantum computers to crack the encryption. Quantum computers are powerful machines that can process data much faster than traditional computers. As a result, they are capable of quickly breaking the encryption generated by ECC. This means that data encrypted using ECC is vulnerable to attack from quantum computers.
Strengths of ECC
Despite the potential risks posed by quantum computers, ECC still has several advantages. First, it is much more secure than traditional cryptography methods. This is because it uses a mathematical equation to generate a pair of public and private keys. This equation is much more difficult to crack than a traditional encryption algorithm. Additionally, ECC is much faster than traditional cryptography methods, making it ideal for use in time-sensitive applications.
ECC and Quantum Computing
Despite the potential risks of using ECC with quantum computers, there are still measures in place to protect data. For example, many organizations are now using post-quantum cryptography algorithms to encrypt their data. These algorithms are designed to be resistant to attack from quantum computers, making them a much more secure option. Additionally, some organizations are also using hybrid cryptography algorithms which combine traditional and post-quantum cryptography algorithms. These algorithms provide an extra layer of security, making them more resistant to attack from quantum computers.
Conclusion
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a secure form of cryptography which provides users with an extra layer of security when using digital transactions. While the technology is vulnerable to attack from quantum computers, there are still measures in place to protect data. Organizations can use post-quantum cryptography algorithms or hybrid cryptography algorithms to ensure their data is safe from quantum attack.
Frequently Asked Questions about Elliptic Curve Cryptography Quantum Secure
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a form of public-key cryptography which is based upon the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields. ECC is a powerful tool for providing security and privacy in communications and is now widely used in the field of cryptography. ECC is considered to be quantum secure, meaning that it is resistant to attacks by quantum computers.
What is Elliptic Curve Cryptography?
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is a form of public-key cryptography which uses the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields to provide a secure communication. It is a type of encryption that uses sophisticated mathematical equations to protect data and has several advantages over traditional methods, such as faster performance and smaller key sizes. The security of ECC is based on the difficulty of solving certain mathematical problems related to the elliptic curve equation.
How is Elliptic Curve Cryptography Used?
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is used in a variety of applications, such as secure communication protocols, digital signature schemes, and key exchange protocols. It is also used in mobile banking and financial applications, as well as in the internet of things (IoT). In addition, it is used as a secure way to authenticate users on websites and other online services.
Is Elliptic Curve Cryptography Quantum Secure?
Yes, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is considered to be quantum secure, meaning that it is resistant to attacks by quantum computers. This is because the mathematical problems related to the elliptic curve equation are difficult to solve with a quantum computer, making ECC a more secure alternative than other traditional methods. Additionally, ECC can be used to generate shorter keys, which makes it faster and more secure than other forms of encryption.
How Does Elliptic Curve Cryptography Work?
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) works by using the algebraic structure of elliptic curves over finite fields to generate a public key and a private key. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the private key is used to decrypt it. Both keys are generated from the same elliptic curve equation, which is why it is considered to be quantum secure. Furthermore, the keys generated using ECC are shorter than those generated using other forms of encryption, making it faster and more secure.
What are the Advantages of Using Elliptic Curve Cryptography?
The main advantage of using Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is that it is considered to be quantum secure, meaning that it is resistant to attacks by quantum computers. Additionally, ECC can be used to generate shorter keys, which makes it faster and more secure than other forms of encryption. Furthermore, ECC is more efficient in terms of power consumption and memory usage than other forms of encryption. This makes it a great choice for applications that require high security and low power consumption and memory usage, such as mobile banking and financial applications.

Elliptic Curve and Quantum Cryptography – CompTIA Security+ SY0-401: 6.1
In conclusion, the question of whether or not elliptic curve cryptography is quantum secure is a complex one that requires careful consideration. While ECC has proven to be a reliable method of encryption, the rise of quantum computing poses a significant threat to its security. As quantum computers become more powerful, they may be able to break current ECC encryption in a matter of seconds or minutes, rendering it useless.
However, researchers are actively working on developing new forms of ECC that are resistant to quantum attacks. With continued innovation and advancements, it is possible that ECC can remain a viable method of encryption in the face of quantum computing. Ultimately, the future of elliptic curve cryptography and its quantum security will depend on the ongoing efforts of the cryptographic community to stay ahead of potential threats and continue to evolve with the changing landscape of technology.