Paragraph 1:
Are you familiar with the term “colposcopy”? If you’re a woman, chances are you’ve heard it before. A colposcopy is a medical procedure performed on women to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for any abnormal changes. This examination is usually recommended by gynecologists when a woman has an abnormal Pap smear result.
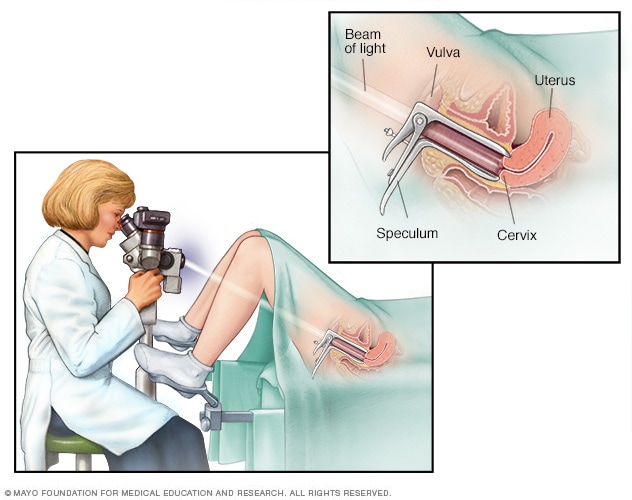
A colposcopy is a non-invasive procedure that uses a special instrument called a colposcope to magnify and illuminate the tissues of the cervix, vagina, and vulva. The procedure is usually performed in a gynecologist’s office and takes about 10-15 minutes. While it may seem intimidating, a colposcopy is a crucial step in detecting cervical cancer and other abnormalities that could potentially lead to cancer. In this article, we’ll go over what to expect during a colposcopy, and why it’s important for women to get this procedure done if recommended by their doctor.
Paragraph 2:
During a colposcopy, the gynecologist will use the colposcope to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva for any abnormal changes. If any suspicious areas are found, the doctor may take a small tissue sample (biopsy) to send to a laboratory for further examination. This biopsy will help determine if the abnormal cells are cancerous or pre-cancerous.
It’s important for women to understand the importance of a colposcopy and to not be afraid to ask questions. Many women may feel anxious or scared before the procedure, but it’s important to remember that a colposcopy is a routine procedure that is performed every day in gynecology offices. By detecting abnormal changes early on, women can receive the necessary treatment to prevent cervical cancer and other related conditions. In the following sections, we’ll cover the preparation and procedure for a colposcopy in more detail.
What is a Colposcopy?
A colposcopy is a visual examination of the cervix, vagina, and vulva using a microscope. It is also known as a cervical smear test. This test is usually done to check for pre-cancerous or cancerous cells in the cervix. It can also be used to identify infections that may be causing cervical abnormalities.
The colposcopy procedure is usually done in a doctor’s office and is usually done after a woman has had an abnormal Pap test result. During the procedure, a doctor will use a colposcope, which is a magnifying instrument with a light. The doctor will use the colposcope to look for any abnormal areas on the cervix, vagina, and vulva.
What to Expect During a Colposcopy
Before the colposcopy procedure, the doctor will explain the procedure and ask a few questions about the patient’s medical history. The doctor may also do a physical examination of the patient’s genitals. During the procedure, the patient will be asked to lie down on an examination table. The doctor will then insert a speculum into the vagina to hold it open and then use the colposcope to examine the cervix, vagina, and vulva.
The doctor may also take a sample of cells from the cervix, which is known as a biopsy. A biopsy is a small sample of tissue that is sent to a laboratory for further testing. The results of the biopsy can help the doctor determine if there are any abnormal cells present. After the procedure, the patient may experience some pain and cramping. The doctor may prescribe a pain reliever for the patient to take after the procedure.
What are the Benefits of a Colposcopy?
Colposcopy is a very important procedure for women’s health. It can help detect pre-cancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix, vagina, and vulva. It can also help to identify infections or other causes of cervical abnormalities. Early detection can help to prevent the development of cancer and other serious health conditions.
Colposcopy is also a safe and non-invasive procedure. It does not require any general anesthesia and usually only takes 15-20 minutes. The risks associated with the procedure are minimal and the benefits can be significant.
Who Should Have a Colposcopy?
Colposcopy is recommended for any woman who has had an abnormal Pap test result. It can also be done if the doctor suspects that there may be a cervical abnormality or infection present. Women who have had pelvic surgery or who have a weakened immune system may also benefit from having a colposcopy.
Women who are pregnant should not have a colposcopy. The procedure should also be avoided in women who have an active vaginal infection or who are menstruating.
Preparing for a Colposcopy
Before the colposcopy procedure, the patient should inform the doctor about any medications, supplements, or herbal remedies that they are taking. It is also important to avoid sexual intercourse, douching, or using any vaginal creams or suppositories for two days before the procedure.
On the day of the procedure, the patient should wear a skirt or loose-fitting pants with no underwear. It is also important to arrive on time for the appointment and to follow any instructions given by the doctor.
What are the Risks of a Colposcopy?
The risks associated with a colposcopy are minimal. However, the patient may experience some pain and cramping during the procedure. The patient may also experience some vaginal bleeding after the procedure. In rare cases, the biopsy may cause an infection or scarring.
Conclusion
A colposcopy is a very important procedure for women’s health. It can help to detect pre-cancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix, vagina, and vulva. The procedure is usually done in a doctor’s office and is usually done after an abnormal Pap test result. The patient should inform the doctor about any medications, supplements, or herbal remedies that they are taking before the procedure. The risks associated with the procedure are minimal and the benefits can be significant.
Frequently Asked Questions
A colposcopy is a visual examination of the vagina, cervix, and vulva performed by a healthcare provider. It is done to diagnose and treat certain conditions of the female reproductive system.
What is a colposcopy?
A colposcopy is a type of medical examination used to get a better view of the cervix and the vagina. It is done by a healthcare professional, such as a gynecologist or a nurse practitioner. The healthcare professional will use a special microscope called a colposcope to take a closer look at the cervix and vagina. The colposcope is used to magnify the area and to look for any abnormal cells or tissue.
A colposcopy may also be used to take a biopsy, or tissue sample, from the cervix or vagina. This sample is then sent to a lab to be examined under a microscope. A biopsy may be used to diagnose a variety of conditions, such as infections, inflammations, and precancerous and cancerous changes.
Why is a colposcopy performed?
A colposcopy is usually performed after an abnormal pap smear result. It can also be done if a woman has symptoms such as unusual vaginal discharge, bleeding between periods, or pain during intercourse. A colposcopy can help diagnose the cause of the symptoms and determine if further treatment is needed.
A colposcopy can also be used to identify and diagnose precancerous and cancerous changes in the cervix and vagina. Early detection and treatment of these conditions can help reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer in the future.
What should I expect during a colposcopy?
Before the colposcopy, your healthcare provider will ask questions about your medical history and any symptoms you may be having. During the colposcopy, you will be asked to lie down on your back on an examination table with your feet in stirrups. Your healthcare provider will use a special microscope, called a colposcope, to examine the cervix and vagina.
The colposcopy procedure should not be painful, but you may feel slight discomfort or pressure. Your healthcare provider may use a vinegar solution to make abnormal areas easier to see. After the examination is complete, your healthcare provider may take a biopsy if necessary.
What happens after a colposcopy?
After the colposcopy, your healthcare provider will discuss the results with you. If a biopsy was taken, the results will be available in a few weeks. Your healthcare provider may recommend further testing or treatment depending on the results of the colposcopy.
In most cases, no further treatment is needed after a colposcopy. However, it is important to follow up with your healthcare provider as recommended to ensure that any abnormalities are monitored and treated if necessary.
Are there any risks associated with a colposcopy?
Colposcopy is generally a safe and effective procedure. However, there are some potential risks associated with a colposcopy, such as bleeding, infection, and scarring. In rare cases, women may experience an allergic reaction to the vinegar solution used during the procedure.
It is important to discuss any potential risks with your healthcare provider before the procedure. Your healthcare provider can help you make an informed decision about whether or not to proceed with the colposcopy.

Colposcopy training video
After undergoing a colposcopy, it is common to feel anxious or uncertain about the results. However, it is important to remember that this procedure is an essential tool in detecting cervical abnormalities and preventing the development of cervical cancer. By providing a clear visual examination of the cervix, a colposcopy can help identify any areas of concern and guide further diagnostic and treatment options.
While the thought of a colposcopy may be daunting, it is essential to prioritize your reproductive health and seek medical attention if necessary. By staying informed about the procedure and its potential outcomes, you can take an active role in your health and ensure that any necessary steps are taken to maintain your well-being. Remember that early detection and treatment can make all the difference in preventing and treating cervical cancer, and a colposcopy is an important tool in achieving this goal.