As technology continues to advance, data processing and storage have become increasingly complex. The need for faster and more efficient computing has given rise to edge/fog computing. Edge/fog computing is an innovative approach that brings computing power closer to the source of data, reducing the need for centralized processing. This approach offers numerous benefits that can revolutionize the way we interact with technology.
One of the main benefits of edge/fog computing is reduced latency. In traditional cloud computing, data is sent to a central server for processing, which can result in significant delays. With edge/fog computing, data is processed locally, reducing the distance it needs to travel and resulting in faster response times. This is particularly important for applications that require real-time processing, such as self-driving cars or industrial automation. By reducing latency, edge/fog computing can improve the performance and reliability of these applications, making them safer and more efficient.
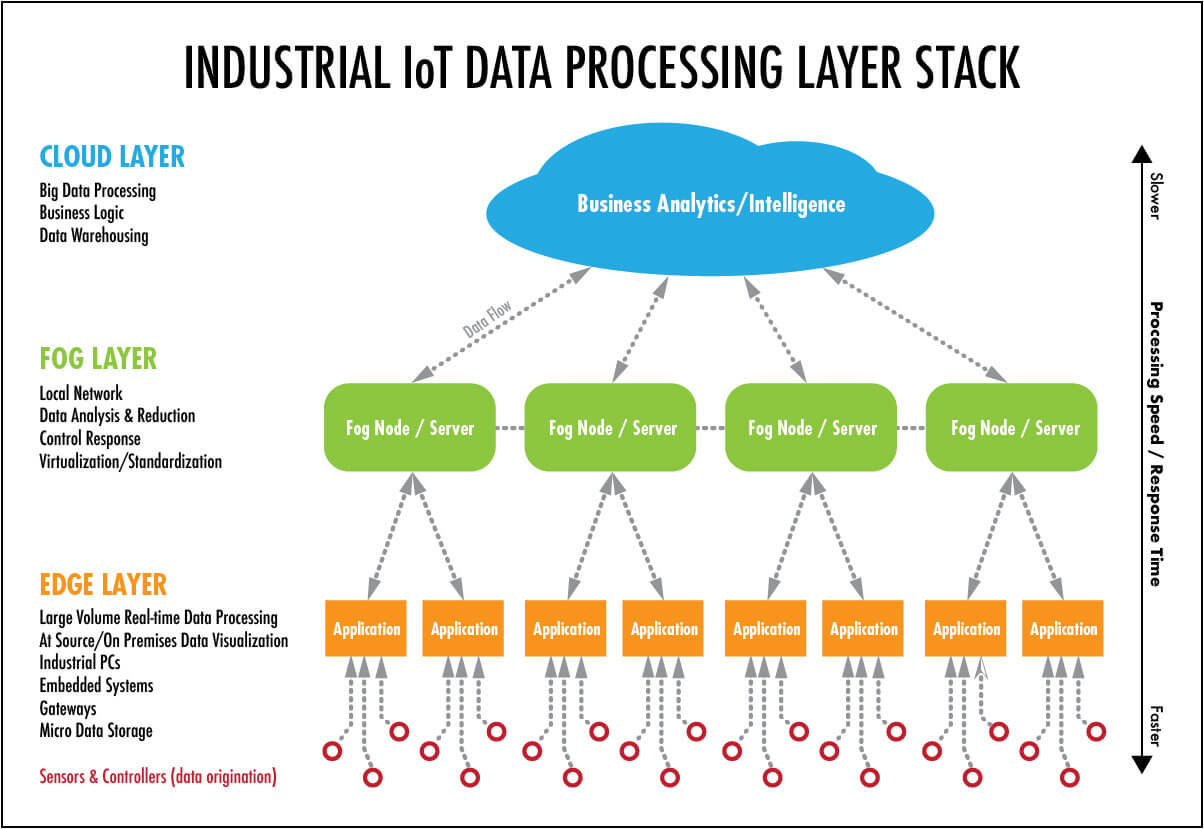
Introduction to Edge/Fog Computing
Edge/Fog computing is a type of distributed computing technology that brings computing power, storage, and other resources closer to the users and devices that need them. It provides a more efficient way to process and store data, which can help reduce latency and improve user experience. Edge/Fog computing is becoming increasingly popular as more businesses and organizations are looking to improve their computing capabilities.
Benefits of Edge/Fog Computing
Reduced Latency
One of the main benefits of Edge/Fog computing is its ability to reduce latency. By bringing computing and data storage closer to users and devices, it eliminates the need for data to travel long distances. This reduces the time it takes for data to be processed and stored, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience.
Another benefit is improved reliability. By having computing and data storage located closer to users and devices, it eliminates the potential for data or information to be lost due to network or server outages. This improves the reliability of the system and helps ensure that data is always available when needed.
Increased Security
Edge/Fog computing also provides increased security. By having computing and data storage closer to users and devices, it eliminates the risk of data being intercepted while in transit. This reduces the risk of data being compromised and helps ensure that sensitive data is kept secure.
In addition, Edge/Fog computing also provides greater control over data. By having data stored and processed closer to users and devices, organizations have more control over who can access the data and how it is used. This helps to ensure that data is only used for its intended purpose and that it is kept secure.
Improved Scalability
Finally, Edge/Fog computing also provides improved scalability. By having computing and data storage closer to users and devices, organizations can quickly scale up or down as needed. This makes it easier for businesses to handle increased or decreased user demand, helping them to stay agile and keep up with changing customer needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edge/fog computing is a type of computing architecture that uses distributed computing nodes to process data closer to the source of the data. This type of computing can provide numerous benefits to users, such as increased efficiency and improved data privacy.
What is Edge/Fog Computing?
Edge/fog computing is a distributed computing architecture that uses multiple nodes to process data closer to the source of the data. This type of computing provides several benefits, including improved efficiency and lowered latency, as well as enhanced data privacy.
Edge/fog computing works by having the processing of data occur at the edge of the network, meaning that data is processed at or near the source. This helps to reduce latency and improve efficiency, as data does not have to travel all the way back to a central server before processing. Additionally, data privacy is improved, as data never leaves its source.
What are the Benefits of Edge/Fog Computing?
The primary benefit of edge/fog computing is improved efficiency and reduced latency. As data is processed closer to its source, it does not have to travel all the way back to a central server before being processed. This leads to improved performance, as data does not need to make multiple round trips before being processed. Additionally, data privacy is improved, as data never leaves its source.
Other benefits of edge/fog computing include improved scalability and more reliable services. As the processing of data is distributed across multiple nodes, the system can be easily scaled up or down as needed. Furthermore, as data is processed close to its source, services can be more reliably provided as the data is not subject to the same risks as data traveling over long distances.
What is the Difference Between Edge/Fog Computing and Cloud Computing?
The primary difference between edge/fog computing and cloud computing is that edge/fog computing processes data closer to its source, while cloud computing processes data in a central location. With edge/fog computing, data is processed at or near its source, meaning that data does not have to travel all the way back to a central server before being processed. This leads to improved performance, as data does not need to make multiple round trips before being processed.
Additionally, edge/fog computing is more secure than cloud computing, as data never leaves its source and is therefore not subject to the same security risks as data traveling over long distances. Furthermore, edge/fog computing is more scalable than cloud computing, as the processing of data is distributed across multiple nodes. This allows the system to be easily scaled up or down as needed.
What is Needed to Implement Edge/Fog Computing?
In order to implement edge/fog computing, several components are needed. These include edge devices, such as sensors, cameras, and other embedded devices, as well as fog nodes, which are responsible for data processing and storage. Additionally, edge/fog computing systems require a platform or software framework that can manage the distributed nodes and allow data to be processed and stored.
Finally, edge/fog computing requires a network that can connect the various nodes and allow data to be transferred between them. This network should be capable of providing low latency and high throughput, as well as being secure and scalable.
What Are the Potential Challenges of Edge/Fog Computing?
The potential challenges of edge/fog computing include security and scalability. As data is processed closer to its source, it is subject to the same security risks as data traveling over long distances. Additionally, as the processing of data is distributed across multiple nodes, the system can be difficult to scale up or down as needed.
Furthermore, edge/fog computing can be difficult to manage as the system is distributed across multiple nodes. This can lead to increased complexity, as nodes need to be managed individually. Additionally, edge/fog computing requires specialized hardware and software, which can be costly and difficult to implement. Finally, edge/fog computing can be difficult to troubleshoot, as the system is distributed across multiple nodes.
In conclusion, edge/fog computing is the future of the internet of things. It offers many benefits such as low latency, improved security, and reduced bandwidth costs. By distributing computing power to the edge of the network, edge/fog computing makes data processing faster and more efficient. It also enables real-time data analysis, which is critical in industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. Furthermore, edge/fog computing allows for greater scalability and flexibility, making it an ideal solution for businesses of all sizes.
As we move towards a more connected world, edge/fog computing will play a crucial role in enabling us to make better use of our data. By bringing processing power closer to the source of the data, we can reduce latency, improve security, and ultimately, make better decisions. With the increasing demand for real-time data analysis and the growth of the internet of things, edge/fog computing will continue to be an essential technology for businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve. As a professional writer, it is clear to me that edge/fog computing is an exciting and promising field, and I look forward to seeing the many ways it will transform the world around us.